Build webhook consumers to subscribe to events
Configure new webhook consumers in Codat and manage existing configuration to receive webhook events
Overview
A webhook consumer is your implementation of a POST endpoint that you built to receive Codat's webhooks. In general, you need one consumer per event type.
This consumer must return a 2XX (status code 200-299) response within 15 seconds of receiving the POST request. We recommend passing the event to an internal message queue so that you can process it in time.
Configure webhook consumer
Once you have built your webhook consumer, configure Codat to send events to this consumer. Navigate to Settings > Webhooks > Events > Configure consumer and click Add endpoint to create a new consumer.
If you are planning to create an application with more than 50 consumers, reach out to your Codat contact so that we can optimize the solution for your use case.
Add the endpoint URL that you want to receive the messages, an optional description, and choose the events that this endpoint should listen to. You must specify a least one event type per endpoint.
Browse our event catalog in the Portal or in our documentation to choose the event types that suit your use case.
You can create a webhook consumer programmatically using our Create webhook endpoint.
If your consumer endpoint is behind a firewall or NAT, you'll need to allow-list IP addresses 4.159.114.108 and 20.117.190.191.
Custom headers
Once you created your webhook consumer, you can use its advanced functionality to add a custom header to the endpoint. This can be useful in the following scenarios:
-
If you are securing your webhook endpoints with an authorization header, you can add it as a custom
Authorizationheader. -
If you are using multiple Codat instances and need to differentiate between them, add a
X-Codat-ClientIdheader with the required client ID. You can find and copy your client ID in the Portal by clicking on your instance dropdown.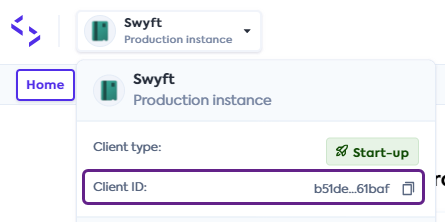
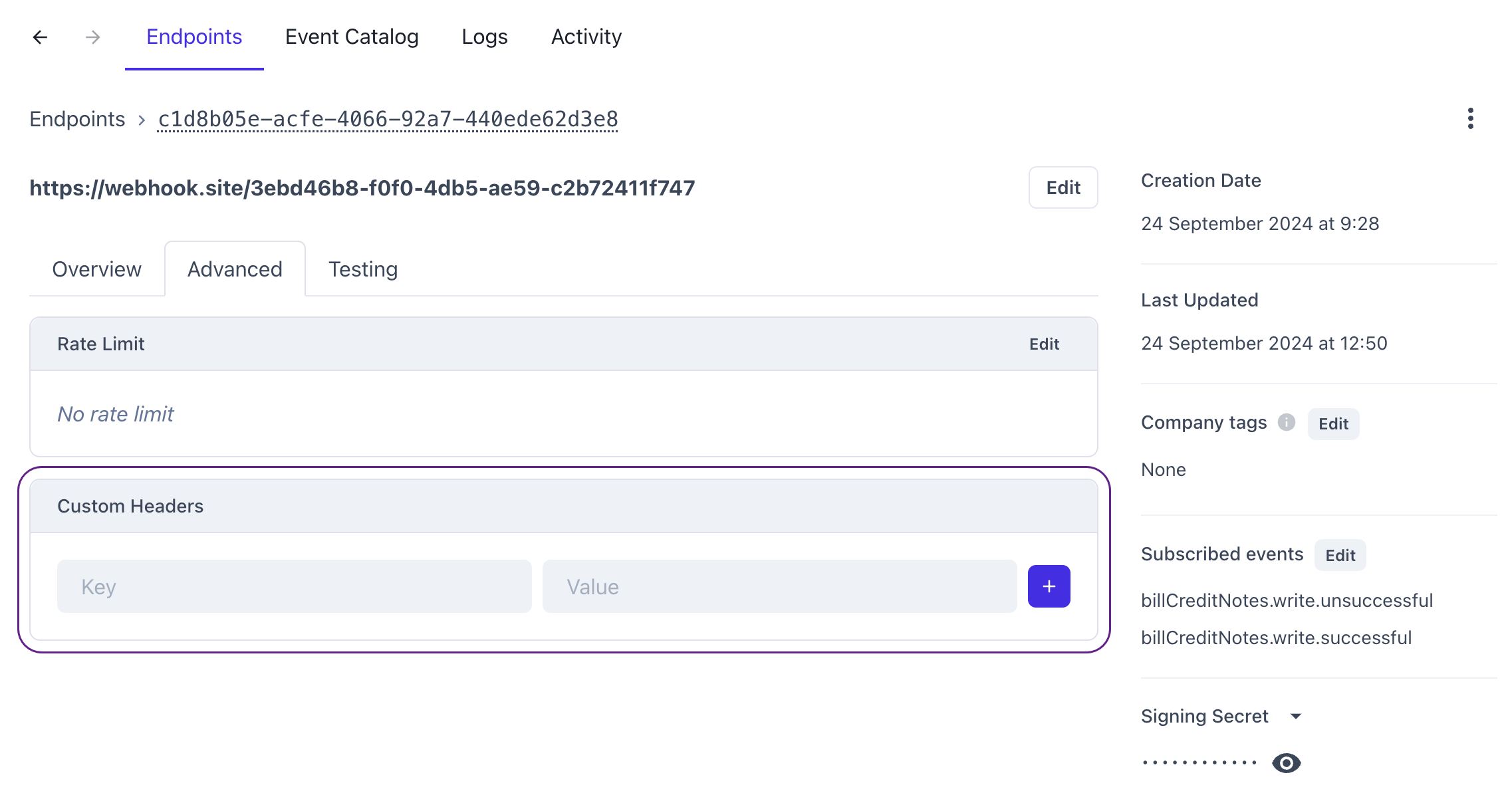
It's not possible to add a custom header via our API. Instead, navigate to Monitor > Webhooks > Events and click on the relevant endpoint to see its detailed view. Then, select the Advanced tab and add your headers to the custom header section.
Filter webhooks by company tags
You can configure a webhook consumer to filter companies based on tags you can add to a company profile. For example, if you want to receive webhooks only for companies tagged with a specific region or service, you can configure the consumer to match those tags.
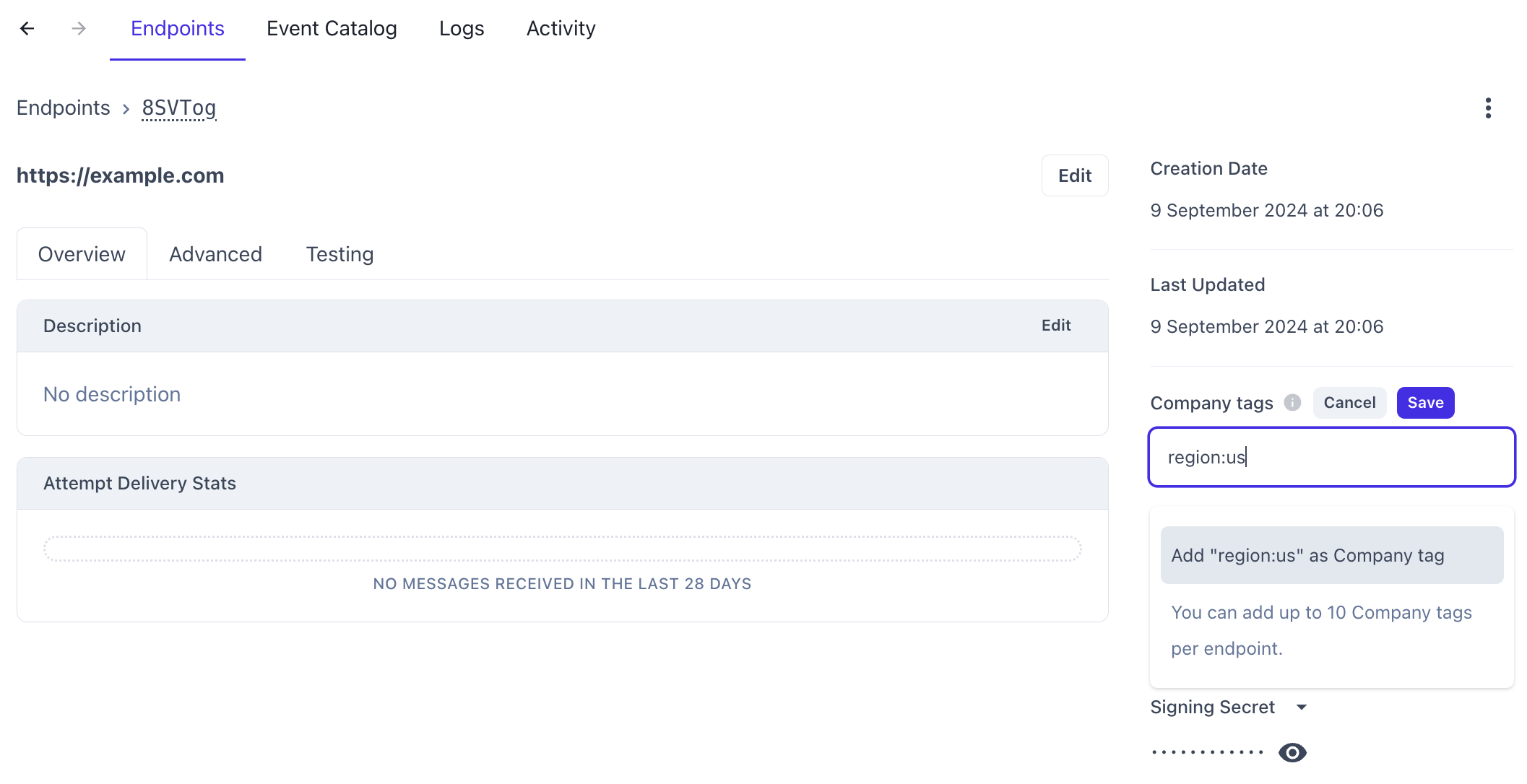
To set this up in the Codat Portal, navigate to Monitor > Webhooks > Events and select the relevant endpoint to view its details. Then, enter the tags you want to filter by in the Company tags field. Each webhook consumer can support up to 10 company tags.
Tags must be formatted as key-value pairs separated by a colon. For example, to route webhooks for companies tagged with a region value of us, set the Company tags field to region:us. Any company tagged with a region value of uk will be ignored.
A message will be delivered every time any of the company’s tags match the tags specified in the webhook consumer. For example, a consumer configured with region:us and service:t2k will still receive messages from a company tagged with region:us and service:minerva because one company tag matches.
View webhook consumers
In the Codat Portal, navigate to Monitor > Webhooks > Events to see the list of all consumer endpoints you have configured.
Alternatively, you can use the List webhooks endpoint to return a list of all consumers that currently exist for your client.
Delete webhook consumers
In the Codat Portal, navigate to Monitor > Webhooks > Events to see the list of your webhook consumers. Click on the one you want to delete, then click on the triple-dot options menu and choose Delete.
Alternatively, you can use the Delete webhook endpoint to delete an existing webhook consumer. You need to provide its valid webhookId as a parameter.
Test a webhook consumer
When adding a webhook consumer endpoint, you may want to test it with an example event to confirm its configuration. Once you have created the endpoint, click on it to see the detailed view, and navigate to the Testing tab.
Next, choose the example event you want to send and click Send example. Once it's sent, you can click into the message to view its payload, attempts, and status.
There are many reasons a message to your endpoint could fail. Have a look at our troubleshooting guide to resolve the most common issues that occur.
Verify webhook signature
A webhook signature is your way to verify that the messages are sent by Codat and helps you avoid impersonation or replay attacks. We sign every webhook and its metadata with a unique security key for each endpoint and include timestamps for when the message attempt occurred.
You can use this signature to verify that the message truly came from Codat before processing it. To do the verification, we suggest using a library called Svix.
Install library
- JavaScript
- Python
- C#
- Go
- Java
- Rust
- Kotlin
- Ruby
- PHP
- CLI
pip install svix
dotnet add package Svix
go get github.com/svix/svix-webhooks/go
Gradle
Add this dependency to your project's build file:
implementation "com.svix:svix:0.x.y"
Maven
Add this dependency to your project's POM:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.svix</groupId>
<artifactId>svix</artifactId>
<version>0.x.y</version>
</dependency>
svix = "0"
Gradle
Add this dependency to your project's build file:
implementation "com.svix.kotlin:svix-kotlin:0.x.y"
Maven
Add this dependency to your project's POM:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.svix.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>svix-kotlin</artifactId>
<version>0.x.y</version>
</dependency>
gem install svix
composer require svix/svix
Verify webhook
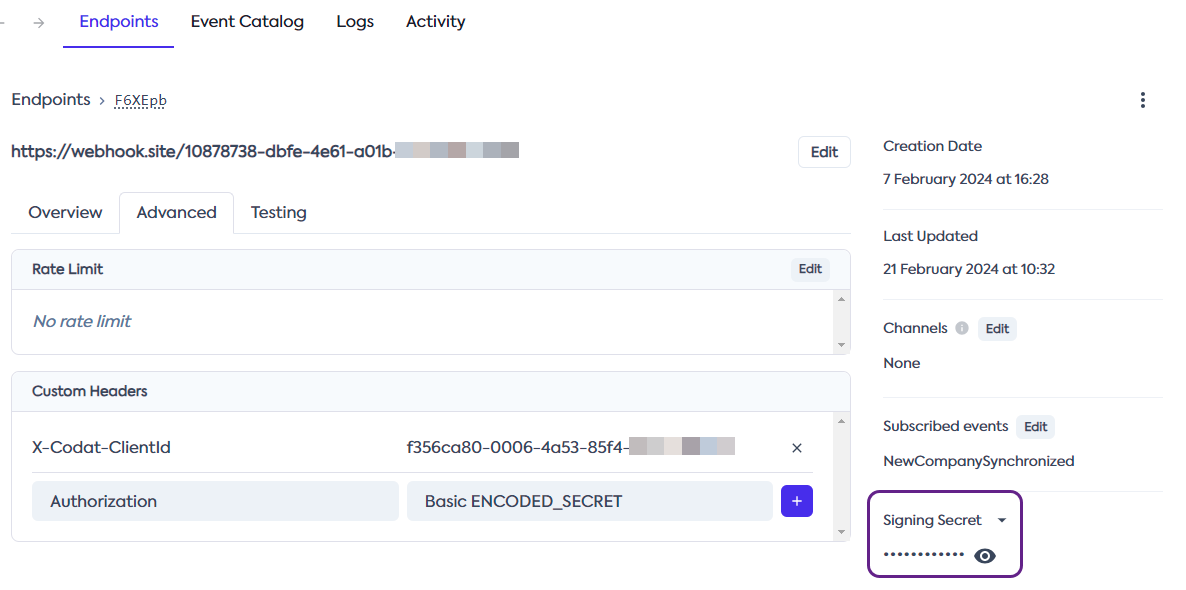
To verify incoming webhooks, retrieve the secret key for your endpoint first.
In the Codat Portal, navigate to Monitor > Webhooks > Events, click the endpoint you want to verify, and copy the Signing secret from the endpoint's detailed view.
Next, you need to pass the secret key, request body, and headers to the verification library as demonstrated below.
You need to use the raw request body when verifying webhooks because the cryptographic signature is very sensitive to changes.
Watch out for frameworks that parse the request as JSON and then stringify it, because this will also break the signature verification.
- JavaScript
- Python
- C#
- Go
- Java
- Rust
- Kotlin
- Ruby
- PHP
- CLI
import { Webhook } from "svix";
const secret = "whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw";
// These were all sent from the server
const headers = {
"webhook-id": "msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek",
"webhook-timestamp": "1614265330",
"webhook-signature": "v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE=",
};
const payload = '{"test": 2432232314}';
const wh = new Webhook(secret);
// Throws on error, returns the verified content on success
const payload = wh.verify(payload, headers);
from svix.webhooks import Webhook
secret = "whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw"
# These were all sent from the server
headers = {
"webhook-id": "msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek",
"webhook-timestamp": "1614265330",
"webhook-signature": "v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE=",
}
payload = '{"test": 2432232314}'
wh = Webhook(secret)
# Throws on error, returns the verified content on success
payload = wh.verify(payload, headers)
using Svix;
using System.Net;
// These were all sent from the server
var headers = new WebHeaderCollection();
headers.Set("webhook-id", "msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek");
headers.Set("webhook-timestamp", "1614265330");
headers.Set("webhook-signature", "v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE=");
var payload = "{\"test\": 2432232314}";
var wh = new Webhook("whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw/Je4ZJEGP1QFb");
// Throws on error
wh.Verify(payload, headers);
import (
svix "github.com/svix/svix-webhooks/go"
)
secret := "whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw"
// These were all sent from the server
headers := http.Header{}
headers.Set("webhook-id", "msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek")
headers.Set("webhook-timestamp", "1614265330")
headers.Set("webhook-signature", "v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE=")
payload := []byte(`{"test": 2432232314}`)
wh, err := svix.NewWebhook(secret)
err := wh.Verify(payload, headers)
// returns nil on success, error otherwise
import com.svix.Webhook;
String secret = "whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw";
// These were all sent from the server
HashMap<String, List<String>> headerMap = new HashMap<String, List<String>>();
headerMap.put("webhook-id", Arrays.asList("msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek"));
headerMap.put("webhook-timestamp", Arrays.asList("1614265330"));
headerMap.put("webhook-signature", Arrays.asList("v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE="));
HttpHeaders headers = HttpHeaders.of(headerMap, BiPredicate<String, String>)
String payload = "{\"test\": 2432232314}";
Webhook webhook = new Webhook(secret);
webhook.verify(payload, headers)
// throws WebhookVerificationError exception on failure.
use svix::webhooks::Webhook;
let secret = "whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw".to_string();
let mut headers = http::header::HeaderMap::new();
headers.insert("webhook-id", "msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek");
headers.insert("webhook-timestamp", "1614265330");
headers.insert(
"webhook-signature",
"v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE=",
);
let payload = b"{\"test\": 2432232314}";
let wh = Webhook::new(&secret)?;
wh.verify(&payload, &headers)?;
// returns Ok on success, Err otherwise
import com.svix.kotlin.Webhook
val secret = "whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw";
// These were all sent from the server
val headersMap = mapOf(
"webhook-id" to listOf("msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek"),
"webhook-timestamp" to listOf("1614265330"),
"webhook-signature" to listOf("v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE=")
)
val headers = HttpHeaders.of(headersMap) { _, _ -> true }
val payload = "{\"test\": 2432232314}";
val webhook = Webhook(secret);
webhook.verify(payload, headers)
// throws WebhookVerificationError exception on failure.
require 'svix'
# These were all sent from the server
headers = {
"webhook-id" => "msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek",
"webhook-timestamp" => "1614265330",
"webhook-signature" => "v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE="
}
payload = '{"test": 2432232314}'
wh = Svix::Webhook.new("whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw")
# Raises on error, returns the verified content on success
json = wh.verify(payload, headers)
// import using composers autoload
require_once('vendor/autoload.php');
// or manually
require_once('/path/to/svix/php/init.php');
// These were all sent from the server
$payload = '{"test": 2432232314}';
$header = array(
'webhook-id' => 'msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek',
'webhook-timestamp' => '1614265330',
'webhook-signature' => 'v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE=',
);
// Throws on error, returns the verified content on success
$wh = new \Svix\Webhook('whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw');
$json = $wh->verify($payload, $header);
export SVIX_AUTH_TOKEN="AUTH_TOKEN"
svix verify --secret whsec_MfKQ9r8GKYqrTwjUPD8ILPZIo2LaLaSw --msg-id msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek --timestamp 1614265330 --signature v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE= '{"test": 2432232314}'